Taiwan University of Science and Technology was established on August 1, 1974, as the first higher education institution dedicated specifically for the technical and vocational education purpose in Taiwan. By expanding the different course offerings since the foundation of the institution, their goal is to create an environment to nurture the next generation of highly skilled engineers and managers in order to meet the needs created by the rapid economic and industrial developments. (Source: www-e.ntust.edu.tw ) Although lightweight demands in plastics manufacturing is continuously rising, the requirement of rigidity and strength is still necessary.  With the addition of fiber, degradable materials can not only help reduce the carbon emission effectively but also enhance the product strength.  In this study, Taiwan University of Science and Technology (Taiwan Tech) selects a degradable material, Poly Lactic Acid (PLA), for simulation and to investigate the effects of fiber orientation on warpage and stress. Utilizing Moldex3D Advanced and Fiber Module to build mesh (Fig. 1), proceed convergence test (Fig. 2) and complete injection molding simulation This case features a specimen made of PLA. PLA has lower crystallization rate, poor strength and heat resistance, so Taiwan Tech team planned to add fiber to improve them. First, Taiwan Tech team verified Moldex3D’s simulation results through experiments, and found consistent filling patterns (Fig. 3). Then they tried to predict the effect of short and long fiber on the product deformation resistance, and find different effects in fiber proportions. Finally, they verified the prediction results of Moldex3D and ANSYS in product deformation and stress. Taiwan Tech knew that adding fiber can enhance the strength of PLA products.  However, they had no idea about what proportion would be the most effective and what type of fiber would be better for strength enhancement.  In this study, they found Moldex3D was able to accurately predict the fiber orientation in the manufacturing phase.  The simulation results can be easily exported from Moldex3D FEA Interface to ANSYS for structural analysis. Taiwan Tech added fiber to pure PLA to enhance the strength.  The results also displayed that compared with short fiber, long fiber had better resistance to deformation (Fig. 4). More addition of fiber will reduce deformation.  In this study, 25% fiber will cause the lowest deformation (Fig. 5). Next, Taiwan Tech utilized ANSYS to verify Moldex3D’s analysis of deformation and stress.  The results showed that the deformation and stress were very identical in ANSYS and Moldex3D. (Fig. 6) From the experience with Moldex3D, fiber effect with different variables can be investigated effectively. Through Moldex3D FEA Interface, users can easily export fiber orientation results and connect to ANSYS for FEA analysis.  This truly is a powerful and reliable integrated solution for considering manufacturing process in FEA prediction.  This case study is also supposed to help facilitate PLA’s applications in the potential market of mobile device covers. Special Welding Machine For Animal Poultry Mesh Special Welding Machine For Animal Poultry Mesh,Poultry Cage Door Welding Line,Welding Mesh Machine,High Speed Welding Machines Jiaoyang Welding Industries Hebei Co., Ltd , https://www.jiaoyangmachine.com
Executive Summary
Challenges
Solutions
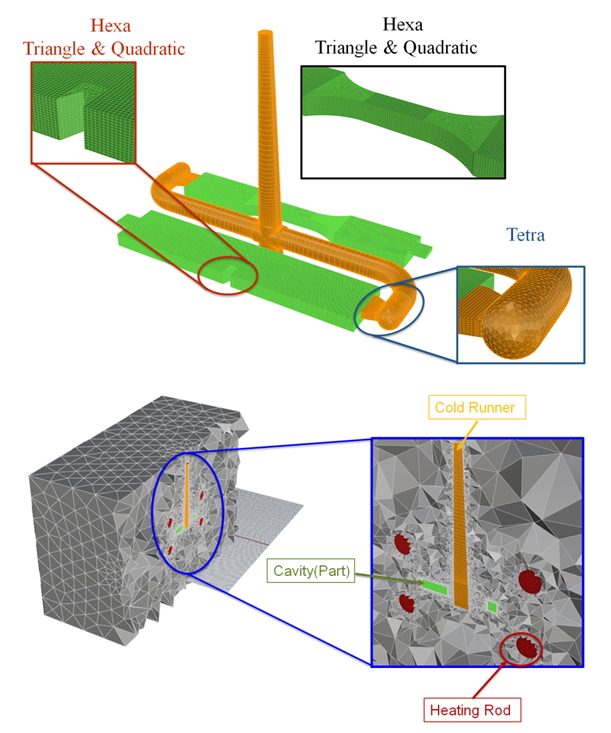 Fig. 1 Mesh building in Moldex3D
Fig. 1 Mesh building in Moldex3D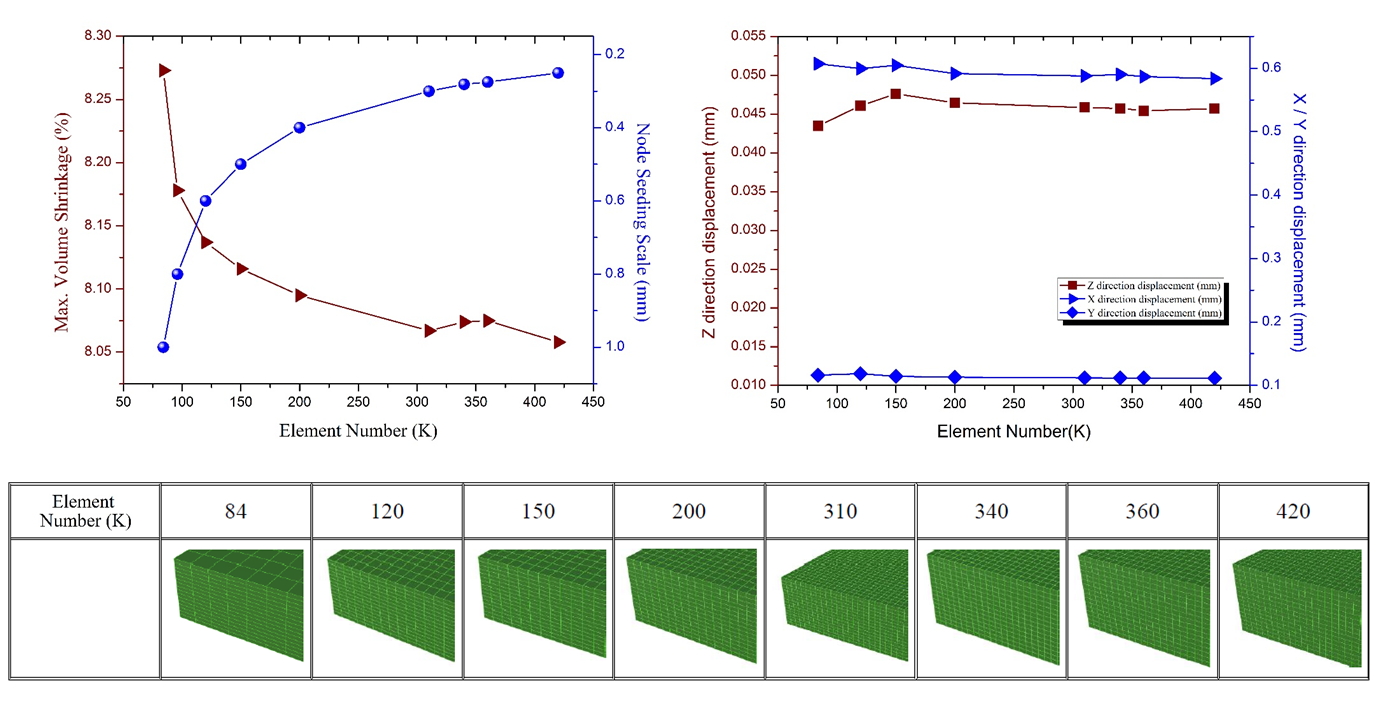 Fig. 2 The element convergence test
Fig. 2 The element convergence testBenefits
Case Study
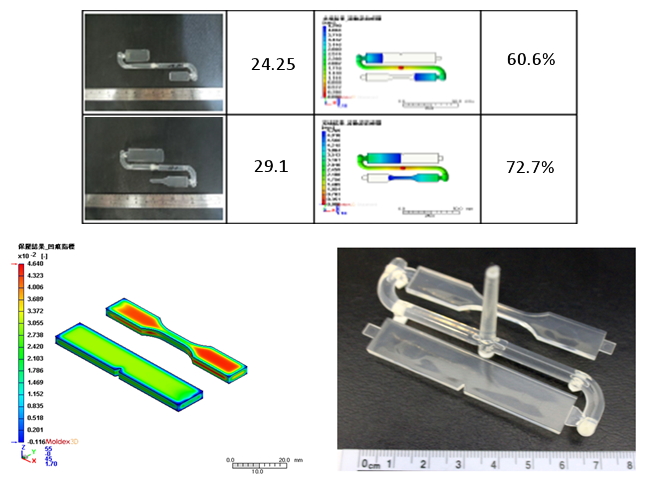 Fig. 3 Moldex3D simulation is verified consistent with the real case in filling pattern and sink mark
Fig. 3 Moldex3D simulation is verified consistent with the real case in filling pattern and sink mark Fig. 4 Compared with short fiber, long fiber has better resistance to deformation
Fig. 4 Compared with short fiber, long fiber has better resistance to deformation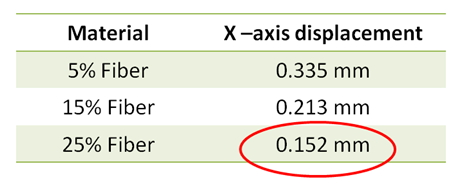 Fig.5 Displacement results of different fiber proportion
Fig.5 Displacement results of different fiber proportion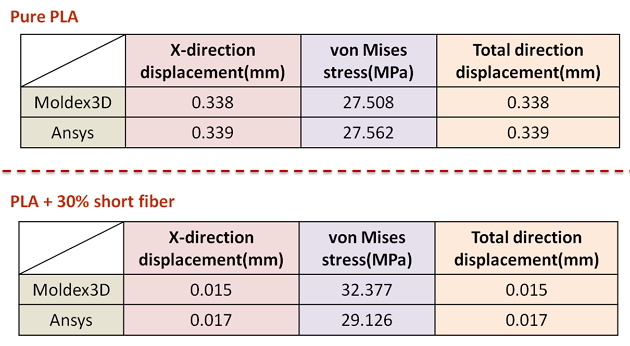 Fig. 6 Moldex3D and ANSYS verification of simulation results
Fig. 6 Moldex3D and ANSYS verification of simulation resultsResults
Integrating Moldex3D and ANSYS to Validate Fiber’s Effects on PLA Products
Customer Profile
