Introduction to the structural performance of wound lead-acid batteries Winding lead-acid battery The wound lead-acid battery is a new product developed in recent years. The working process of lead-acid batteries is the chemical reaction process between lead and acid. In order to increase the specific capacity of the battery, people need to increase the contact area between them as much as possible. For this reason, people have made the method of rolling lead alloy. A very thin lead foil is used as the plate substrate. However, in this way, its mechanical strength is necessarily reduced. In order to solve this problem, the positive plates, the separators, and the negative plates are alternately stacked and wound together. Thus, a wound lead-acid battery in which the battery cell is cylindrical is formed, which is also called a spiral wound lead-acid battery, or a coil electrode lead-acid battery. Rolled lead-acid batteries have always been a technological trump card in developed countries. According to reports, the United States began researching wound lead-acid batteries in the 1960s. A few developed countries in the West have also applied coiled lead-acid batteries in special fields such as military (armored vehicles, tanks, submarines, etc.). In military tests, this special battery can still quickly start a tank or other military equipment after being broken by bullets. After the test of the Gulf War, this battery pack was called the "US Strategic Battery Pack." Structural performance of wound lead-acid batteries The wound lead-acid battery has a spiral structure. It uses a plate of only about 1 mm and is wound by high pressure. Since the grid material used is pure lead or lead-tin alloy, it is relatively soft and is favorable for winding. The electrolyte is a solid acid, and the electrode plate is bundled with the solid acid and rolled up to make a unique spiral winding. Because it uses a solid acid, it avoids the problem of freezing of the electrolyte, and has excellent low temperature performance, and can work normally at a low temperature of -55 ° C. The working principle of the wound lead-acid battery is the same as that of the traditional lead-acid battery. It is only an improvement in the manufacturing process, and it is these improvements that make it have better characteristics than the traditional battery, mainly in the following several aspects: (1) Excellent high and low temperature performance The wound lead-acid battery can operate from -55 ° C to 75 ° C. Since the wound lead-acid battery adopts the spiral winding technology, the gap between the plate and the plate is extremely small, and the acid is solid acid, and can be adsorbed by the glass fiber mesh, and the whole structure is extremely tight. Therefore, at high temperatures, there is substantially no bubbling phenomenon, and at low temperatures, no liquid acid can be frozen, and there is no problem of reduced current output. According to the US SAE test standard, the coiled lead-acid battery can be safely and quickly started and pulled in the range of -55 ° C to 75 ° C, while the applicable temperature range of the ordinary battery is generally only -10 ° C to 40 ° C. This is also the root cause of its ability to solve the low temperature conditions of the above-mentioned automatic water measuring and reporting system. (2) Charging is very fast The wound lead-acid battery can be charged with more than 95% of electricity in 40 minutes. Since the internal resistance of the wound lead-acid battery is extremely low, the charging current can be substantially fully accepted, and its own capacity is large, so there is no current limitation during charging, and the general fast charging time can be fully loaded in about 1 hour. However, the internal resistance of an ordinary battery is high, so part of the charging current will be converted into heat energy, and the charging time is generally at least 6 hours. The wound lead-acid battery is made of high-purity lead, so its side reaction is much smaller than that of an ordinary battery, so the battery can be charged with a small current, and the charging efficiency can be more than 90% even in rainy days. (3) Long life The floated lead-acid battery can be designed for a float life of more than 8 years. Since the coiled lead-acid battery has a very large active lead area, its recovery ability after discharge is also extremely strong. According to the US SAE standard, in the J240 test, the number of times of the wound lead-acid battery is as high as 15,000 times. Compared with ordinary batteries, the power and the number of starts are about 2000-4000 times, and the wound lead-acid battery has a stronger advantage. (4) Small self-discharge electrode Since the internal resistance of the wound lead-acid battery is extremely small, the self-discharging electrode itself is small when it is not in use. The wound lead-acid battery can be placed for two years without charging, so in a sense, it is truly maintenance-free. Ordinary batteries must be charged for up to 1-2 months. Due to the above excellent performance, the wound lead-acid battery has been widely used in various fields such as hybrid electric vehicles, power tools, instrumentation, and wind power generation.
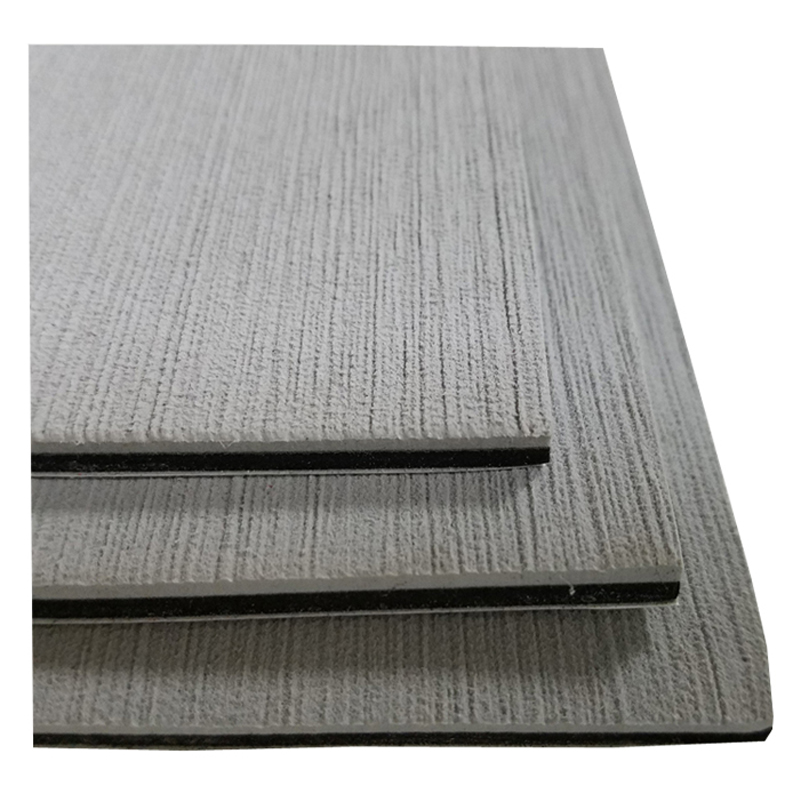
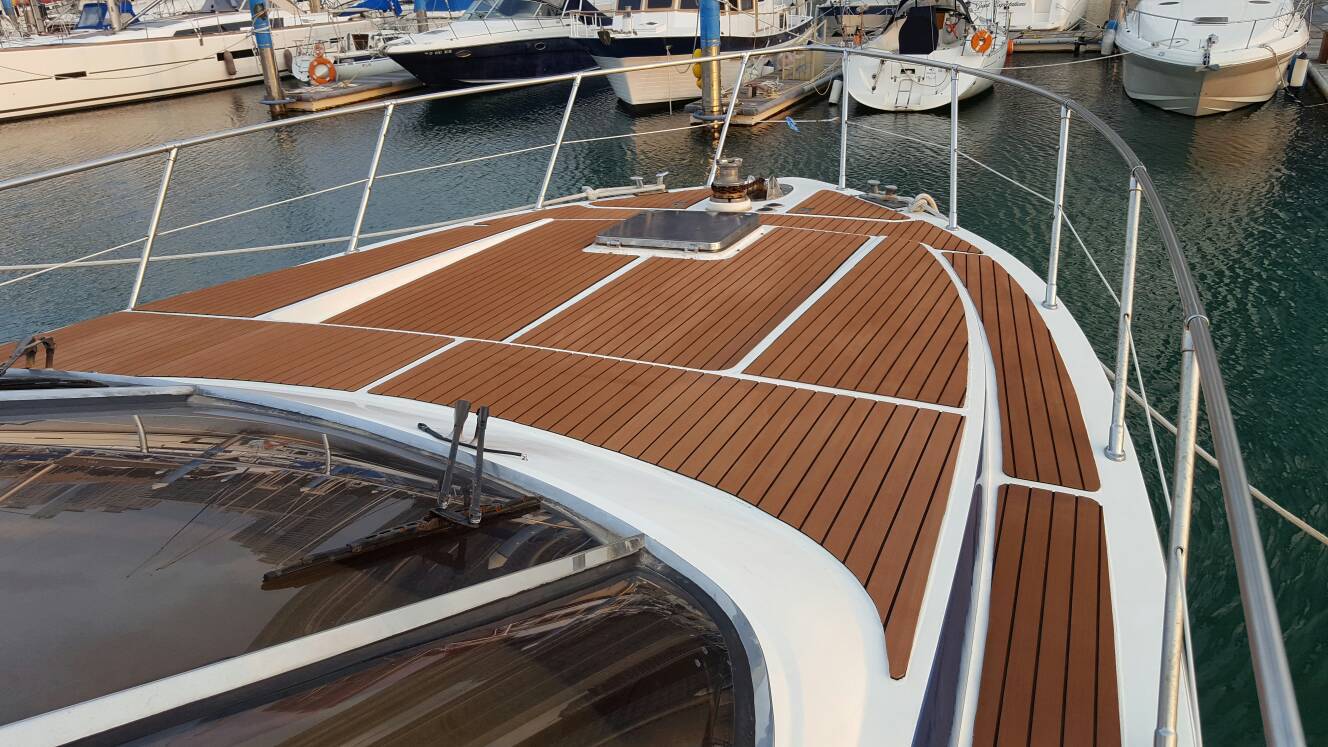
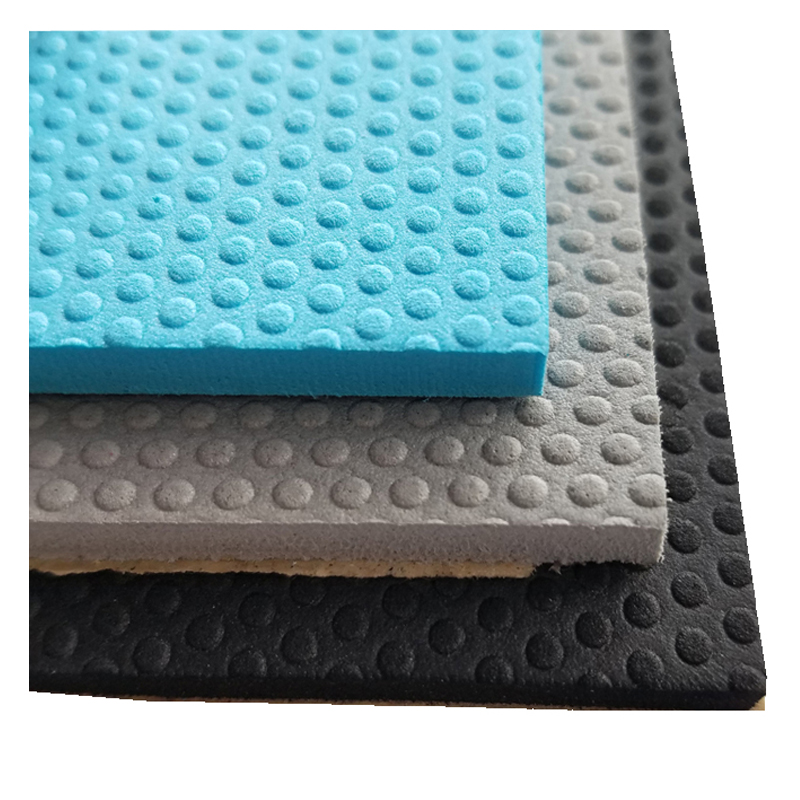
EVA Boat Flooring is a new type marine sheet flooring for boat or yacht. Made from marine grade UV-resistant, closed cell EVA foam material, it is waterproof, antibacterial, comfortable, durable and non-skid.
Basically, the boat flooring has two different textures available, which is brushed and embossed. The sheets can be cut into size to fit the shape of boat decking, then peel the adhesive on the backing and stick it.
Normally the EVA marine sheet can be applied on the boat decking, or with a thicker material, it can be applied as helm station pad, seat pad, or coming bolster pad. What's more, it can be also applied on the edge of swimming pool, cause it can provide a good traction and safety when the feet is wet.
Eva Boat Flooring,Eva Yacht Flooring,Marine Sheet,Diy Boat Flooring,Boat Floor Mat,Boat Mat Huizhou City Melors Plastic Products Co., Limited , https://www.evafoammaster.com


Introduction to the structural performance of wound lead-acid batteries
