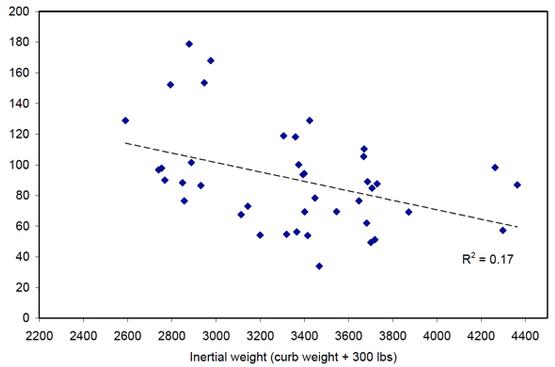
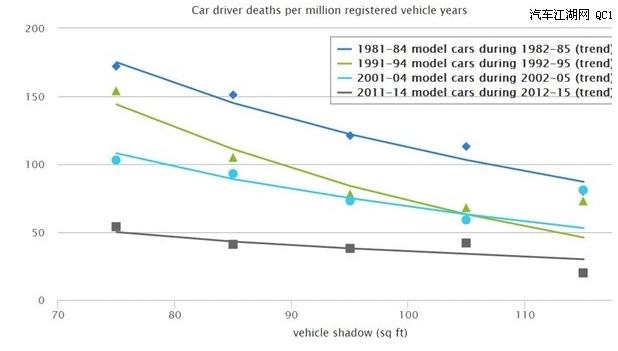
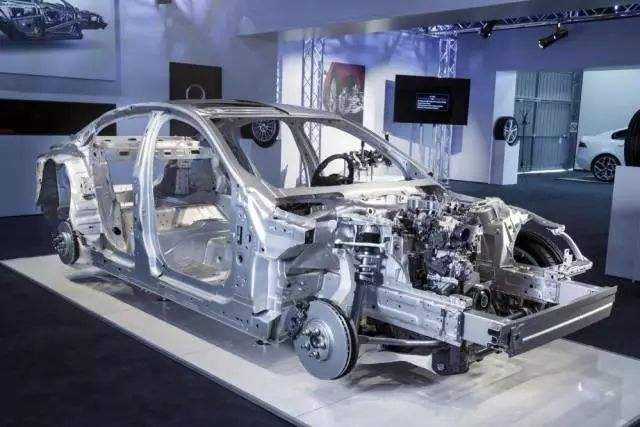
Hurricane "Elma" landed on the Florida Keys of the United States on the morning of September 10, local time. As one of the most dangerous storms in the Atlantic Ocean, "Elma" stormed 210 kilometers per hour and struck Florida, Florida's eastern city of Miami. There was a heavy storm on the day. Not long ago, on August 25, the strongest hurricane “Harvey†in 12 years also landed in Texas, which caused a serious impact on the auto market in the last week of August. Houston, the fourth largest city in the United States, has become a country with a reputation as one of the major markets for light trucks. As a result, sales of SUVs dropped. In August, sales of SUVs in the United States fell by 3.8% year-on-year to 145,000 units. On the third weekend of August, before Hurricane Harvey landed in Texas, LMC, Edmunds, and Kelly Blue Book all predicted that light vehicle sales in the United States would increase by 1% year-on-year in August. However, a typhoon "Harvey" has blown away the hope that the US auto industry will grow for the first time this year. In the end, August light vehicle sales in the United States were 1.485 million, a year-on-year decrease of 1.8%. In the first eight months of this year, a total of 113.558 million units were sold, a year-on-year decrease of 2.7%. The expected growth of the auto market fell again. In the current global environment of the urgent requirements for energy conservation and emission reduction, the fuel economy policies of various countries are continuously tightening. Experiments have shown that for each 10% reduction in vehicle weight, fuel efficiency can be increased by 6%-8%, and for every 100 kg of vehicle trim quality, fuel consumption per 100 kilometers can be reduced by 0.3-0.6 liters. Therefore, lightweighting, as an important way for vehicles to achieve energy conservation and consumption reduction, has attracted the attention and admiration of major car companies. In the "Made in China 2025" jointly issued by the national ministries and commissions, lightweighting has become an important direction for the development of the automobile industry. The impact of the hurricane on the decline in US light vehicle sales caused us to think. Does lightweighting have some drawbacks when successfully achieving energy conservation and consumption reduction? Vehicle safety is the core element and prerequisite for automobile manufacturing. It is also the lifeline for car companies to operate steadily. What impact does lightweighting have on vehicle safety? Today we will take a closer look. The lighter the vehicle, the less secure it is? At present, there are opinions that the lighter the vehicles are, the less safe they are. According to relevant media reports, foreign experts in relevant fields conducted three times in 1997, 2003, and 2004 respectively to analyze the correlations between car weights and safety, through historical vehicles. The accident rate and casualty rate were analyzed by logistic regression. Finally, it was concluded that if the car were to reduce the weight of 100 pounds, it would cause an additional 1,000 deaths a year. Is it really the truth? Is the lighter the vehicle, the lower the safety factor? The specific situation we look at Figure 1. Figure 1. Effect of vehicle weight on risk factors of different models In Figure 1, the horizontal axis represents the weight of the vehicle, and the vertical axis represents the risk factor (ie, the accidental death rate per million vehicles per year). As can be seen from the analysis, there is no direct linear relationship between the risk factor and vehicle weight for different vehicle types. The vehicle that feels safe is actually not as safe as it was supposed to be. For further understanding, let us look at Figure 2. Figure 2. Horizontal axis for vehicle size and weight ratio, vertical axis for death rate per million people In FIG. 2 , the horizontal axis is the vehicle size and weight ratio, and the vertical axis is the death rate per million people. As can be seen from Fig. 2, the mortality rate per million people is lower as the vehicle size and weight ratio increases. This shows that the safety of the vehicle does not depend on the weight of the vehicle body alone, but also closely relates to the size of the vehicle. The safety factor of the vehicle needs to be considered based on the difference in the structure of the vehicle, and is graded according to the size and weight. For the prevailing conditions of contemporary models, heavier vehicles generally have higher levels, larger body sizes, and can provide greater cushioning and energy-absorbing areas in the event of a collision and are more secure. At the same time, due to the greater mass of the car body, the impact of changes in the state of motion of the vehicle is smaller and the impact on the vehicle personnel is even smaller. According to the statistics of the United States IIHS, the accidental death rate of small/mini cars has been reduced to a great extent compared with the past decade, but it is still at a disadvantage compared to the larger models of the same generation. In terms of vehicle braking, due to the reduction in vehicle weight due to weight reduction, the deceleration system consumes less energy when decelerating at the same speed. Under the same brake conditions, the braking effect is greater, and the braking distance is shortened. The braking performance is obviously improved. After the vehicle is lightened, the active safety performance will be improved. Therefore, in the face of potential accidents and potential threats, lighter vehicles can be circumvented with better acceleration, braking, and controllability, but heavier vehicles will prevail slightly when inevitable collisions occur. . It is worth noting that, under the same conditions, the higher the general vehicle weight is, the greater the change in body size and quality cannot be ignored. When the vehicle has a constant length, width, height, and wheelbase, it can be seen from Fig. 2 that lightweighting is beneficial to safety. It can be seen that vehicle safety cannot be measured simply by the weight of the vehicle. The safety design of the car itself, the impact energy absorbing structure, the high-strength material and the load transmission capacity, and the integrity of the passenger compartment after the collision are all of safety. Impact, and these factors are in fact not directly related to the size of the car's weight. At present, lightweight technology is not a simple weight loss, but is a convergence of various types of cutting-edge manufacturing technologies and processes in the automotive industry, ensuring that safety is also a prerequisite for lightweight implementation. Pros and cons of lightweight materials Usually, the OEM engineers mainly optimize the configuration of lightweight materials, vehicle structure design and manufacturing processes to achieve vehicle safety and lightweight. Among them, lightweight materials include high-strength steel (thermoformed steel), light alloy (aluminum alloy, carbon fiber, magnesium alloy), memory metal (microcrystalline steel), engineering plastics, ceramics, glass fiber and so on. These materials have advantages and disadvantages, affecting the lightening process of automobiles to varying degrees. Let's look at the specifics below. Steel materials High-strength steel has obvious advantages compared with aluminum, magnesium alloy and carbon fiber in anti-collision performance, processing technology and cost, and can meet the need of weight reduction and improvement of collision safety performance. In the same structural design, the high-strength steel longitudinal beams absorb more energy and the A-pillar B-pillars are not easily deformed. The disadvantage is that it is not as lightweight as aluminum, magnesium alloy and carbon fiber. Aluminum alloy The advantages of aluminum alloys include light weight and wear resistance, good elasticity and corrosion resistance, excellent impact resistance, excellent processability, and 100% recyclability. They are lightweight materials that car companies are keen to use. The disadvantage is that the anti-load bearing capacity is relatively weak, and the anti-load bearing capacity of aluminum alloys is far from that of steel. Therefore, even if it is an all-aluminum car, its chassis is still generally made of steel. In addition, the aluminum alloy preparation process is complicated and the cost is relatively high. At present, more models of aluminum alloys are used in high-end cars. magnesium alloy The advantage of magnesium alloys is that magnesium alloys are excellent lightweight materials for automobiles and are the lightest structural materials for engineering applications. The density of pure magnesium is 2/3 of that of aluminum and 1/4 of that of steel, which is very close to the density of engineering plastics. And magnesium alloys have higher specific strength than aluminum alloys and steel. Magnesium alloy castings can weigh about 25% less than aluminum castings without reducing the strength of the parts. Magnesium alloys also have excellent welding and casting properties, good vibration and impact absorption, good resistance to dents, and easy machining. The disadvantage is that the problem of high price and high temperature creep resistance has not yet been effectively solved. Therefore, it is currently mainly used in automobile parts such as instrument panel bases, fan frames, steering wheel shafts, and lamp brackets. carbon fiber The advantage of carbon fiber is its ultra-light weight and high strength. It is a new type of high-strength, high-modulus fiber containing more than 95% carbon. BMW applied carbon fiber material to a large area on i3 pure electric and i8 hybrid supercars. The fatal drawback is that it is costly and can only be applied to ultra-luxury models at present. The high construction cost has limited the popularity of this material, but with the development of technology, the cost of carbon fiber is expected to decrease. At the same time, because carbon fiber is a brittle material, it will be directly broken due to excessive force, and it can hardly be repaired after being damaged, making it difficult to recycle it. In addition, the high strength of carbon fiber is limited to the axial direction, and its radial strength is low. Engineering plastics The advantages of engineering plastics are lightweight, rust-proof, shock-absorbing, and flexible design. They are widely used in auto parts, especially interior parts. The disadvantage is that the strength and appearance are not enough. All in all, the ultimate goal of automotive manufacturing is to achieve the best balance between vehicle safety, performance, cost, and weight. It is believed that with the development of lighter vehicles and advancement in science and technology, lighter weight technology is becoming more and more perfect, and automotive engineers will surely have perfect solutions. Laser Marker Machine,Desktop Laser Marker,Laser Marker Price Shandong Lixu International Trading Co., Ltd. , https://www.sdhxmachinery.com

![]()

![]()




![]()
The United States hurricane caused light vehicle sales decline in lightweight and difficult to get rid of?
